M16 Nut Dimensions: Hex & Thin Series
This charts covers both the Regular Series (DIN 934 / ISO 4032) for standard load-bearing applications and the Thin or Half Series (DIN 439 / ISO 4035), which is ideal for jam nut or lock nut configurations or applications with limited vertical clearance. The thread dimensions comply with DIN 13-1 (coarse), DIN 13-21 (fine series), and ISO 68-1 standards to ensure a precise fit and reliable engagement across high-capacity metric fastening systems.
Disclaimer: Actual dimensions, including the width across flats (spanner or wrench size), nut height, and thread tolerance may vary depending on the specific manufacturing class and material — always verify with the official product datasheet before use or buying.

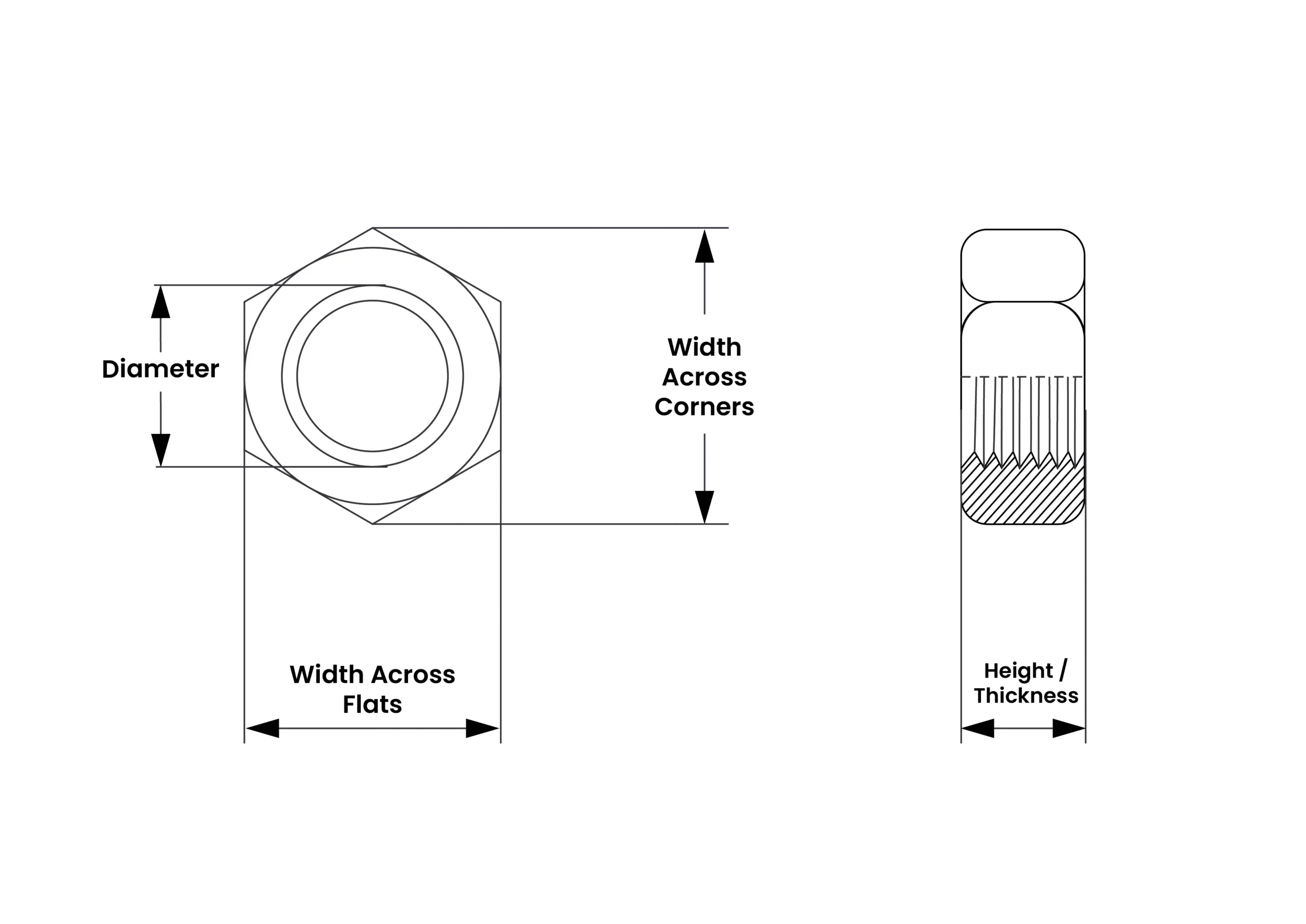
| M16 x 2.0 Hex Nut – DIN 13-1/ISO 68-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Major Diameter | 16 | 16.501 |
| Pitch Diameter | 14.701 | 14.913 |
| Minor Diameter | 13.835 | 14.21 |
| Thread Pitch | 2.0 | |
| M16 x 1.5 Hex Nut – DIN 13-21/ISO 68-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Major Diameter | 16 | 16.406 |
| Pitch Diameter | 15.026 | 15.216 |
| Minor Diameter | 14.376 | 14.676 |
| Thread Pitch | 1.5 | |
| M16 x 1.0 Hex Nut – DIN 13-21/ISO 68-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Major Diameter | 16 | 16.304 |
| Pitch Diameter | 15.35 | 15.51 |
| Minor Diameter | 14.917 | 15.153 |
| Thread Pitch | 1.0 | |
| Metric to Inch Converter | |
|---|---|
| Enter mm to convert to inches | |
Frequently Asked Questions
What size wrench or spanner do I need for an M16 nut?
An M16 hex nut requires a 24 mm wrench or socket. While some specialized heavy-duty variants may vary, 24.00 mm is the standard width across flats (s) for both DIN 934 and ISO 4032 standards.
What is a jam nut?
A jam nut is a low-profile hex nut, typically from the Thin Series (DIN 439), that is used to lock a standard nut in place. By tightening a standard nut against a jam nut, you create internal tension between the threads of both nuts and the bolt. This “jams” the assembly together, providing a mechanical lock that prevents loosening caused by vibration or rotation.
Can a Thin Series nut handle the same torque as a Regular nut?
No. Because the Thin Series has fewer threads in contact with the bolt, it has a lower proof load. For an M16 fastener, which often carries significant loads, using a thin nut as the primary fastener is dangerous as the threads are likely to shear or strip under high tension. Always use a Regular Series nut for structural integrity.
Why is M16 a standard in structural engineering?
M16 is often the “baseline” size for steel-to-steel connections in building frames and industrial platforms. It provides a massive jump in clamping force and tensile strength over M12 or M14, making it suitable for supporting significant dead loads and resisting shear forces in construction.