M27 Bolt & Screw Dimensions: Diameter & Head Size
Disclaimer: Actual dimensions and tolerances may vary slightly depending on head style (e.g., Hex Head, Heavy Hex, Anchor Bolts), manufacturer, or material grade — always verify with the official product datasheet before use.
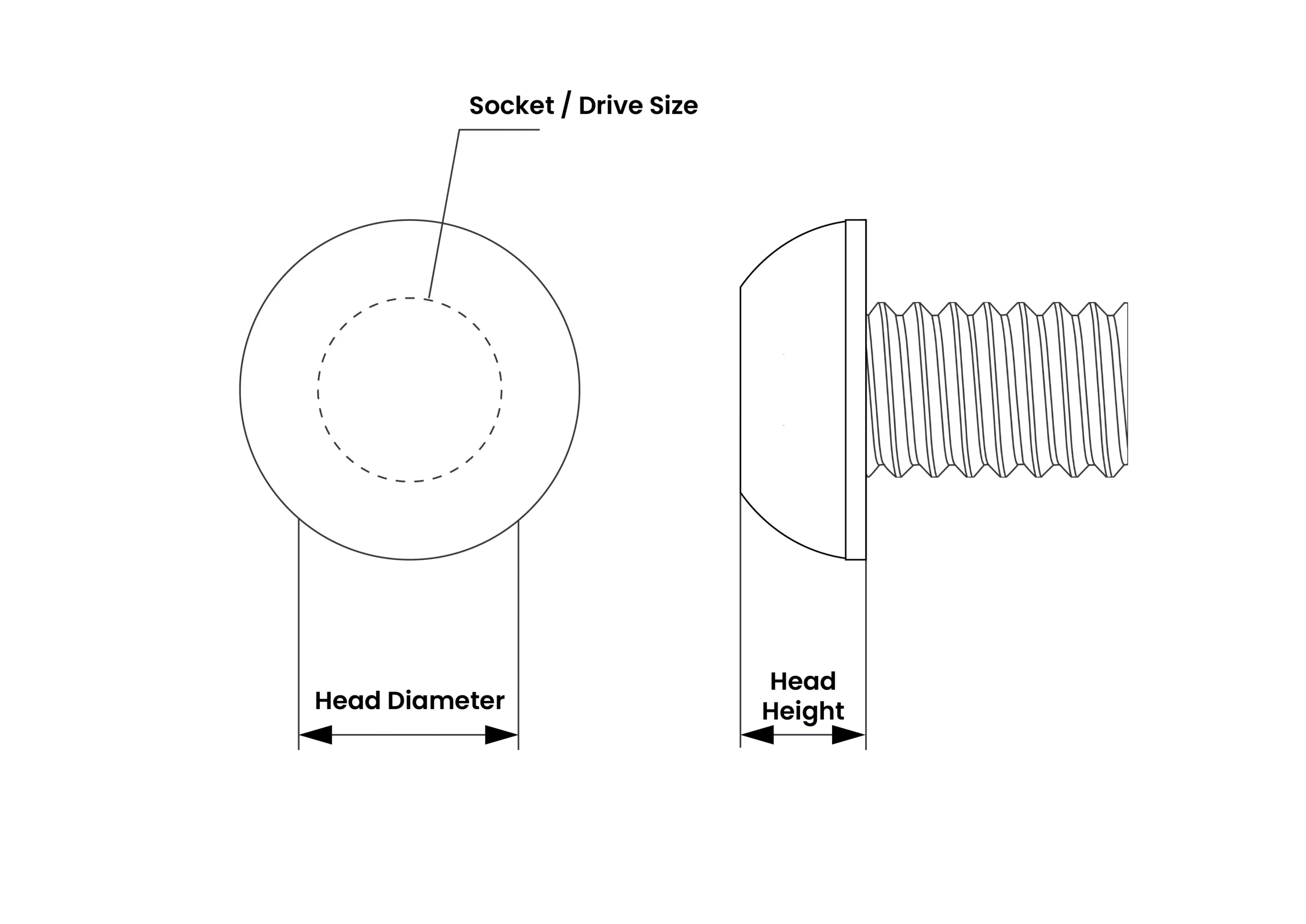
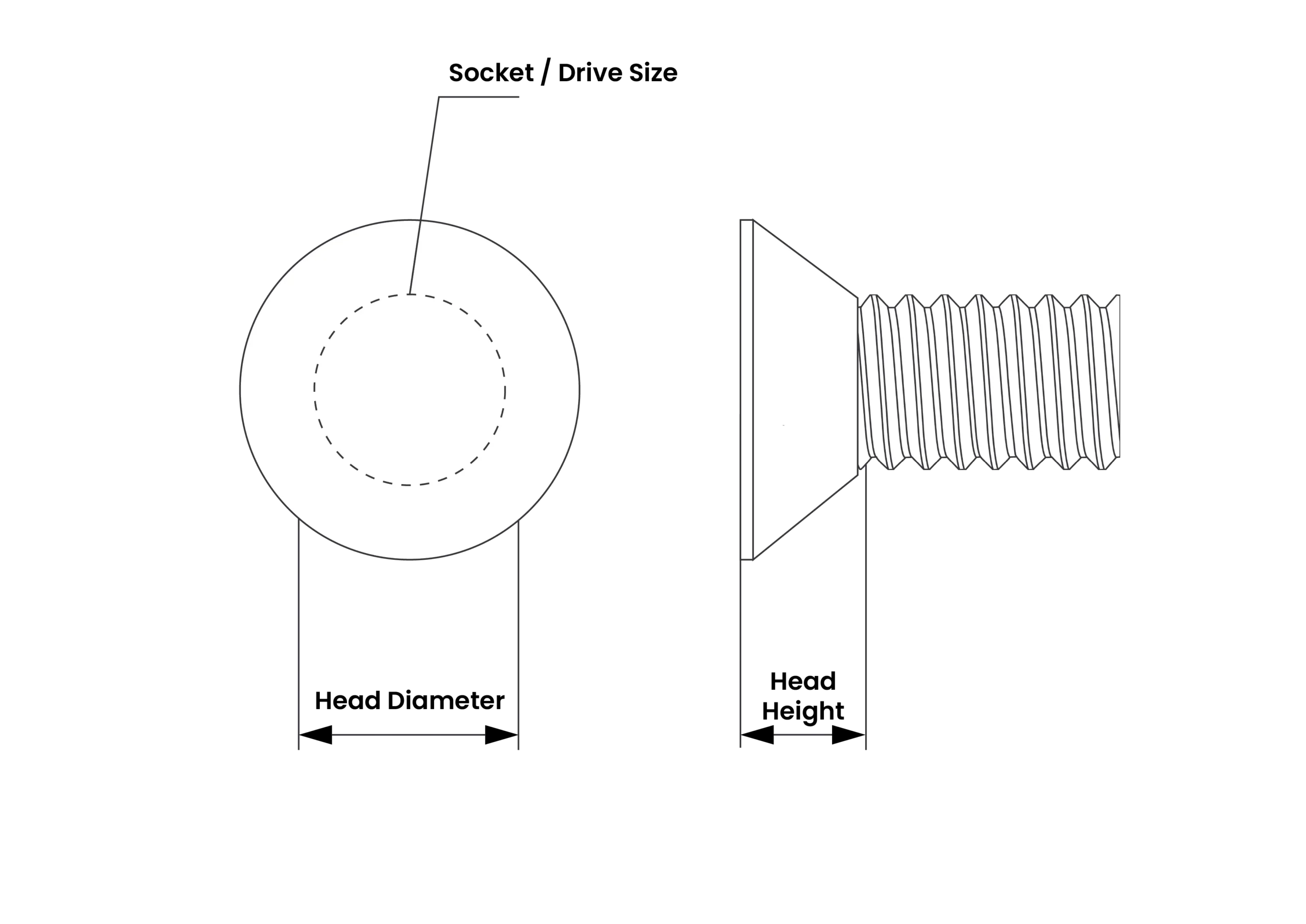
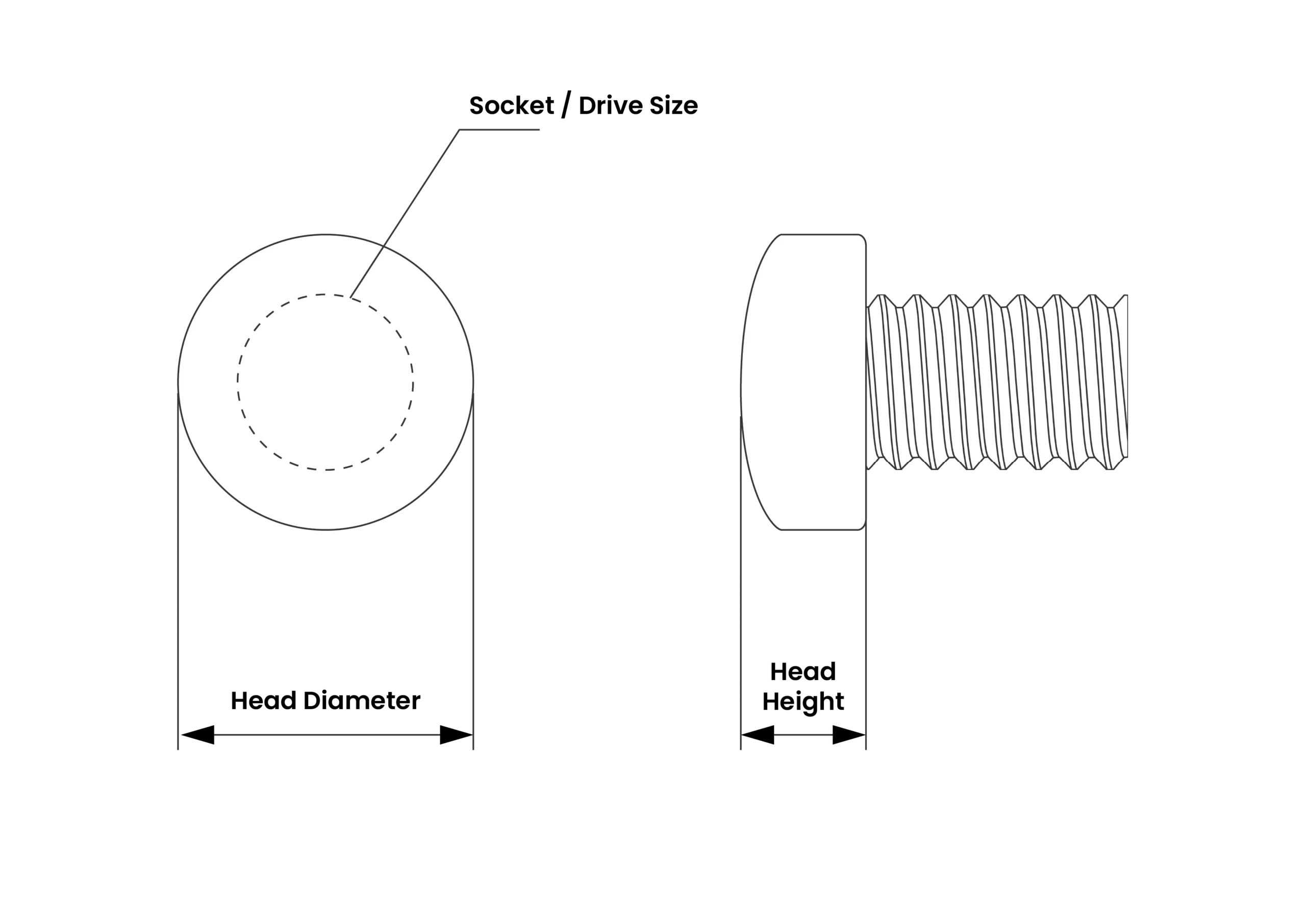
| M27 x 3.0 Screw & Bolt – DIN 13-1/ISO 68-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Major Diameter | 26.577 | 26.952 |
| Pitch Diameter | 24.803 | 25.003 |
| Minor Diameter | 22.955 | 23.704 |
| Thread Pitch | 3.0 | |
| Major Diameter | 26.577 | 26.952 |
| Pitch Diameter | 24.878 | 25.003 |
| Minor Diameter | 23.03 | 23.704 |
| Thread Pitch | 3.0 | |
| M27 x 2.0 Screw & Bolt – DIN 13-21/ISO 68-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Major Diameter | 26.682 | 26.962 |
| Pitch Diameter | 25.493 | 25.663 |
| Minor Diameter | 24.261 | 24.797 |
| Thread Pitch | 2.0 | |
| Major Diameter | 26.682 | 26.962 |
| Pitch Diameter | 25.557 | 25.663 |
| Minor Diameter | 24.325 | 24.797 |
| Thread Pitch | 2.0 | |
| M27 x 1.5 Screw & Bolt – DIN 13-21/ISO 68-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Major Diameter | 26.732 | 26.968 |
| Pitch Diameter | 25.844 | 25.994 |
| Minor Diameter | 24.92 | 25.344 |
| Thread Pitch | 1.5 | |
| Major Diameter | 26.732 | 26.968 |
| Pitch Diameter | 25.899 | 25.994 |
| Minor Diameter | 24.975 | 25.344 |
| Thread Pitch | 1.5 | |
| M27 x 1.0 Screw & Bolt – DIN 13-21/ISO 68-1 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Major Diameter | 26.794 | 26.974 |
| Pitch Diameter | 26.199 | 26.324 |
| Minor Diameter | 25.583 | 25.891 |
| Thread Pitch | 1.0 | |
| Major Diameter | 26.794 | 26.974 |
| Pitch Diameter | 26.244 | 26.324 |
| Minor Diameter | 25.628 | 25.891 |
| Thread Pitch | 1.0 | |
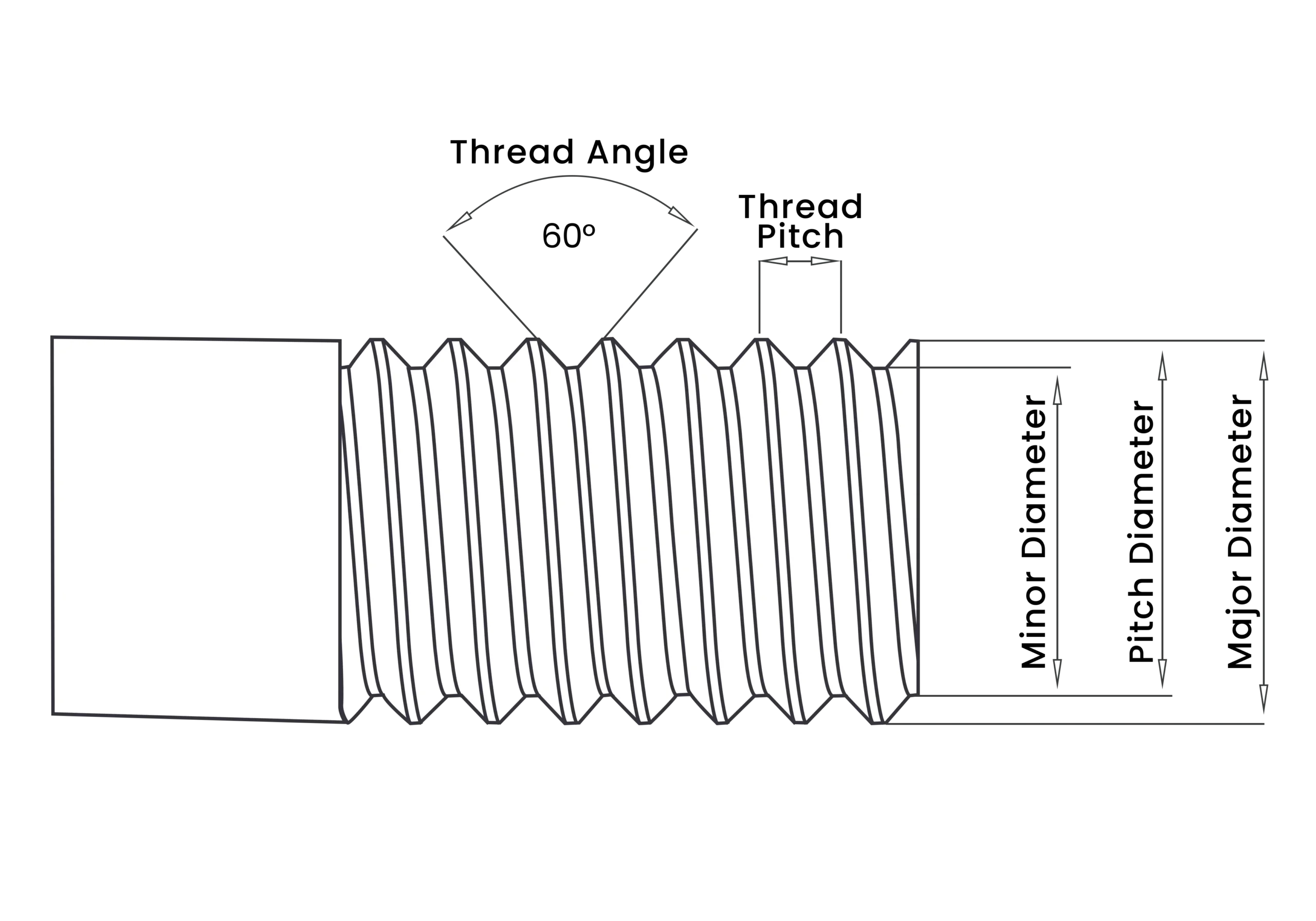
- Major Diameter – The largest diameter of the external thread, measured crest to crest. This defines the nominal size (e.g., M12 which is 12 mm of nominal major diameter).
- Pitch Diameter – The diameter of an imaginary cylinder where the thread thickness equals the space between threads. This is the critical dimension for thread fit (Tolerance classes 2A/3A for Imperial; 6g/4g6g for Metric).
- Minor Diameter – The smallest diameter of the external thread, measured root to root. This represents the core strength of the fastener and is the theoretical maximum diameter of the tap drill.
- Thread Pitch – The distance from a point on one thread to the corresponding point on the next.
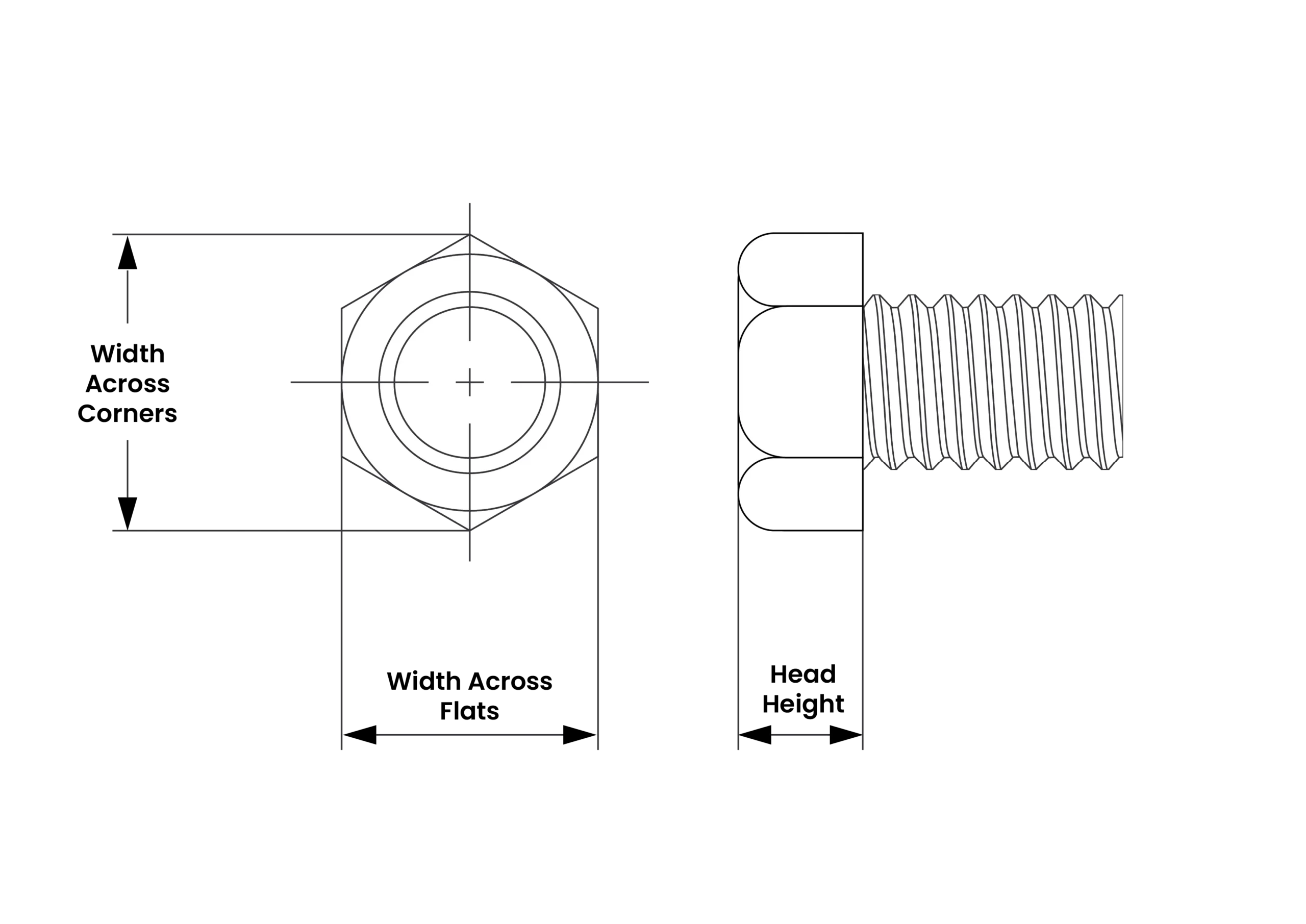
| Hex Head – DIN 933/ISO 4017 | ||
|---|---|---|
| Dimension | Size (mm) | |
| Min | Max | |
| Width Across Flats | 40 | 41 |
| Width Across Corners | 45.2 | Not specified |
| Head Height | 16.65 | 17.35 |
| Metric to Inch Converter | |
|---|---|
| Enter mm to convert to inches | |
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the tap drill size for M27 screws or bolts?
For metric fasteners, the recommended tap drill size can be calculated using this formula: Major Diameter – Thread Pitch. For an M27 x 3.0 (Coarse), the recommended tap drill is 24.00mm. For an M27 x 2.0 (Fine), the recommended drill size is 25.00mm.
What clearance hole size is needed for an M27 screw or bolt?
For an M27 fastener, a 28.00mm drill bit is utilized for a Close Fit, a 30.00mm bit is used for a Normal Fit, and a 32.00mm bit is recommended for a Loose Fit. A Normal Fit is the industry standard to ensure the bolt shank passes through the assembly without binding while maintaining structural alignment.
What is the equivalent size for M27 in inch (imperial)?
For size M27, the nearest inch (imperial) match is 1-1/16". This particular size has a maximum major diameter of 26.988 mm (1.0625 inch), which means the measurement offset is only about 0.013 mm (0.00053 inch).
While these diameters are nearly identical, metric and imperial fasteners are not interchangeable. They utilize fundamentally different thread systems: Imperial fasteners are measured by Threads Per Inch (TPI), whereas metric fasteners use Thread Pitch. Mixing metric and imperial hardware is strongly discouraged, as it can lead to damaged components, reduced load-bearing capacity, and catastrophic mechanical failure.
What is the difference between a bolt and a screw?
The difference is based on the intent of the fastener’s use; If the primary intent is for the fastener to pass through an unthreaded hole and be assembled with a nut, it is a Bolt. In this application, you usually hold the head and turn the nut to apply tension. But if the primary intent is for the fastener to be installed into a threaded (tapped) hole, it is a Screw. In this application, the connection is tightened by turning the head of the fastener itself.